Data Logger - Part 3 - Visualization
Introduction
This is the third in a series of posts to build a simple data logger system for temperature and relative humidity.
Posts in the series:
- Part 1 - Hardware - build a data logger for recording temperature and humidity using a Raspberry Pi
- Part 2 - Storage - send data to an Amazon Timestream database
- Part 3 - Visualization - viewing your data in a graphical form
Libraries
The following libraries are used in the script:
- awswrangler - queries date from Amazon Timestream database.
- matplotlib - used for plotting data.
- pandas - provides powerful data structures and data analysis tools to deal with datasets (included with awswrangler).
import awswrangler as wr
from matplotlib import pyplot as pltSetup Constants
DATABASE_NAME = "DataLoggerDB"
TABLE_NAME = "IoT"
QUERY_DATE = "2021-11-15"
QUERY_SENSOR = "001"Get Data
Uses awswrangler to query data and put into a Pandas DataFrame.
# Get date from Timestream database
SELECT_SQL = f"SELECT * FROM {DATABASE_NAME}.{TABLE_NAME} WHERE SensorId = '{QUERY_SENSOR}' AND DATE(time) = '{QUERY_DATE}' ORDER BY time ASC"
df = wr.timestream.query(SELECT_SQL)
print('Raw data from Timestream')
print(df)Clean Data
Steps to clean the data before it is plotted.
# Data cleaning - Remove date and seconds
df['time'] = df['time'].apply(lambda t: t.strftime('%H:%M'))
# Data cleaning - Pivot table so Temperature and Relative Humidity are columns
df = df.pivot(index="time", columns="measure_name", values="measure_value::double")
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Data cleaning - Remove rows where there null values
df.dropna()
# Data cleaning - Smooth out data before plotting
df['Temperature'] = df['Temperature'].interpolate(method='polynomial', order=2)
df['Relative Humidity'] = df['Relative Humidity'].interpolate(method='polynomial', order=2)
print('Cleaned data for plotting')
print(df)Plot Data
Plot the cleaned data using matplotlib.
# Plot data
figure, axes = plt.subplots(2)
figure.suptitle(f'Temperature and Relative Humidity\n({QUERY_SENSOR} - {QUERY_DATE})')
df.plot(kind='line',x='time',y='Temperature', ax=axes[0], color='tab:blue', legend=None)
df.plot(kind='line',x='time',y='Relative Humidity', ax=axes[1], color='tab:orange', legend=None)
axes[0].set_ylabel('Temperature ($^\circ$C)')
axes[0].set_xlabel(None)
axes[1].set_ylabel('Relavive Humidity (%)')
axes[1].set_xlabel('Time')
plt.show()Usage
$python3 data_plotting.pyDisplays the raw data from the Timestream database.
Raw data from Timestream
SensorId Unit Location measure_name time measure_value::double
0 001 DegC Office Temperature 2021-11-15 12:00:00.944 23.0
1 001 % Office Relative Humidity 2021-11-15 12:00:05.976 65.0
2 001 DegC Office Temperature 2021-11-15 12:01:19.028 23.0
3 001 % Office Relative Humidity 2021-11-15 12:01:24.388 65.0
4 001 DegC Office Temperature 2021-11-15 12:02:30.264 23.0
.. ... ... ... ... ... ...
633 001 % Office Relative Humidity 2021-11-15 18:32:16.509 62.0
634 001 DegC Office Temperature 2021-11-15 18:33:21.821 23.0
635 001 % Office Relative Humidity 2021-11-15 18:33:26.713 65.0
636 001 DegC Office Temperature 2021-11-15 18:34:34.591 23.0
637 001 % Office Relative Humidity 2021-11-15 18:34:39.462 57.0
[638 rows x 6 columns]Displays the cleaned data ready for plotting.
Cleaned data for plotting
measure_name time Relative Humidity Temperature
0 12:00 65.000000 23.0
1 12:01 65.000000 23.0
2 12:02 66.000000 23.0
3 12:03 65.000000 23.0
4 12:05 65.000000 23.0
.. ... ... ...
343 18:30 63.644859 23.0
344 18:31 62.000000 23.0
345 18:32 62.000000 23.0
346 18:33 65.000000 23.0
347 18:34 57.000000 23.0
[348 rows x 3 columns]Final plot displaying tha data.
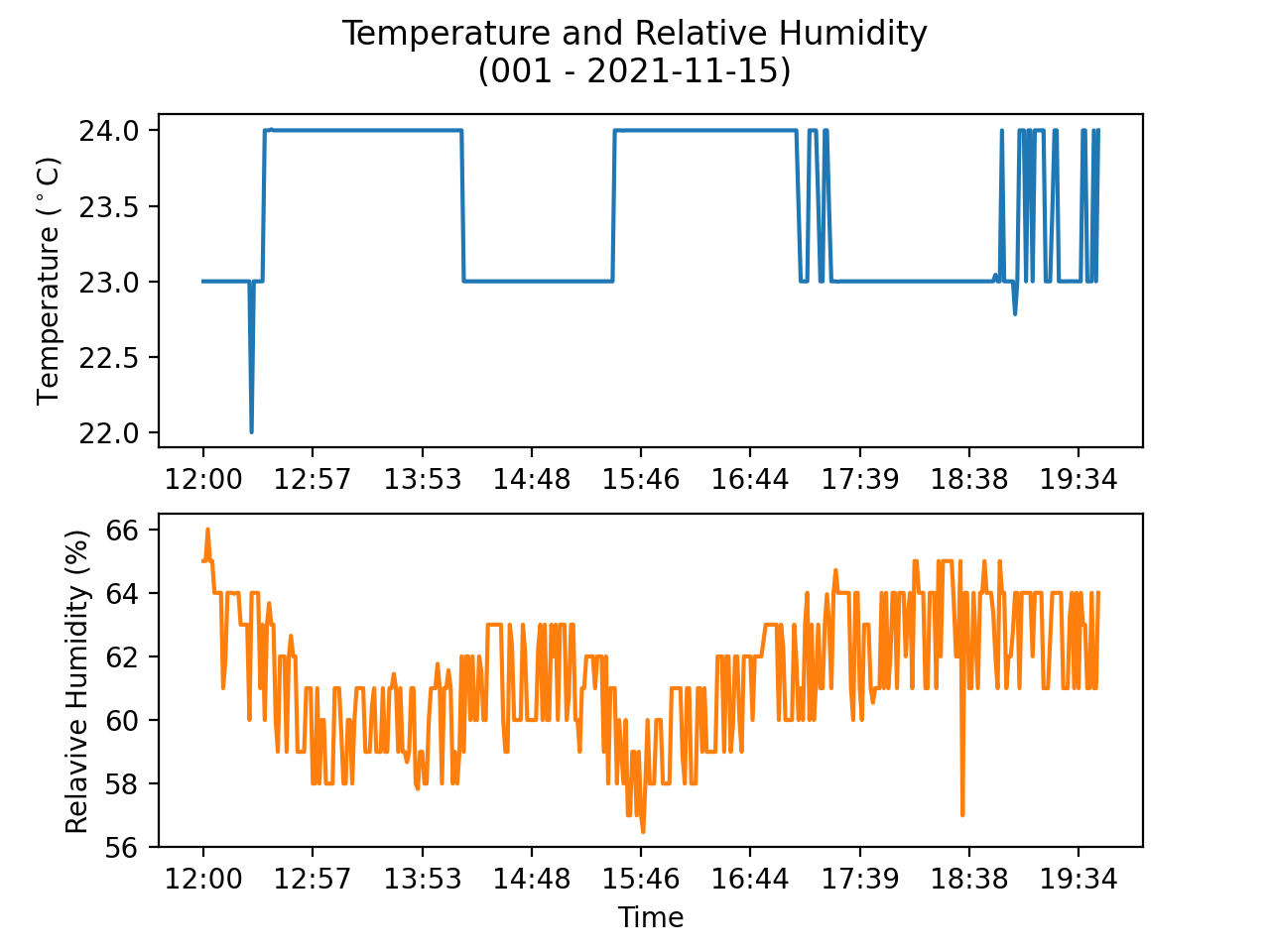
Summary
This post describes now to visualize the Temperature and Relative Humidity readings from the sensor attached to the Raspberry Pi from the data logged to the Amazon Timestream database.
The code for this post is available on GitHub.
